|
Photon Needle helps to treat breast cancer
Sunday, 15 January 2012 15:35
|
|
|
Unfortunately for many breast cancer patients tumour resection does not end their problems. Usually a several-week-long conventional radiotherapy treatment must follow the surgery to decrease the risk of cancer relapse. The Photon Needle X-ray generator developed in NCBJ can be applied intra-operative, so that the postoperative irradiation can be avoided, at least in some cases. „Lifetime of our generator may be estimated for at least several thousand hours. It is a very good result as compared to commercially available competing equipment”, said Eng. Piotr Mazerewicz of NCBJ. Photon Needle is an Electronic X-ray Source for Brachytherapy (ESB; brachytherapy is radiotherapy using sources inserted into the to-be-killed tumours). Once breast tumour is resected, the surgeon inserts tip of the Photon Needle ESB into the postoperative cavity. The entire device is small enough to be mounted on a convenient 3D manipulator than can be freely relocated, oriented and blocked at any position selected by the physician. Personnel leaves the operating room for the irradiation time (about 20 minutes). Actual values of dose-rate, accumulated dose, and other parameters of the process are continually computer-monitored and may be remotely controlled during the entire irradiation session. After that the surgical site is stitched, and the patient may go home already the next day. Photon Needle ESB is actually an electron accelerator. Electrons accelerated by about 50,000 V potential difference are directed into a several cm long tube of 6 mm ID. End of the tube is closed with a silver-plated beryllium cap, whose centre is the target point for the beam. Electrons suddenly decelerated by silver atoms generate X-rays. The radiation is emitted nearly isotropically i.e. evenly at all angles around the point of origin. Beryllium is a very light element that only insignificantly attenuates all but the smallest energy X-rays, so that the ESB-generated radiation can kill cancer cells within the postoperative lesion. „Homogenous and isotropic distribution of the emitted radiation around the device tip helps the physician to precisely plan the irradiation session”, points out Mazerewicz. „Electron beam diameter is less than 1 mm. To keep it exactly at the target, the Photon Needle ESB is equipped with some features that prevent the beam to be shifted off the target by even such subtle effects as a change of the Earth magnetic field inside the tube resulting from a change of orientation of the device”, said Professor Mieczysław Słapa from NCBJ. Should any of the device operating parameters exceed its permissible range, ESB safeguards will turn the device automatically off. Small dimensions are not only significant advantage at any operating room, but also make the entire device easily portable; according to current needs, the device may be easily transported to other clinics. The developed in Świerk ESB demonstrator is ready for first clinic tests scheduled for 2012. The Photon Needle ESB is being developed within the framework of the „Accelerators & Detectors” project currently run in NCBJ Świerk. The project is co-financed by EU within the Innovative Economy Operational Programme framework. One of the project main objectives is to construct demonstrators of three various types of medical accelerators for cancer radiotherapy. The other objective is to construct a demonstrator of a stationary TIR/container scanner system and a demonstrator of a mobile detector of explosives to be applied at border checkpoints to fight illegal trafficking of hazardous substances. Total budget of the project scheduled for 2008-2013 is 85.6 million PLN, including UE assistance in the amount of 67.5 million PLN. |





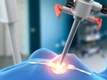 Second generation of the Photon Needle miniature medical accelerators that produce X-ray radiation of some precisely fixed parameters are being developed within the framework of the „Accelerators & Detectors” project currently under development in National Centre for Nuclear Research in Świerk (NCBJ). The device may be applied during surgery of breast cancer patients to kill cancer cells that might remain after the surgery (the so-called intra-operative radiotherapy).
Second generation of the Photon Needle miniature medical accelerators that produce X-ray radiation of some precisely fixed parameters are being developed within the framework of the „Accelerators & Detectors” project currently under development in National Centre for Nuclear Research in Świerk (NCBJ). The device may be applied during surgery of breast cancer patients to kill cancer cells that might remain after the surgery (the so-called intra-operative radiotherapy).


